16 Evaluate square root of (3)^4 √(−3)4 ( 3) 4 17 Evaluate square root of 45 √45 45 18I know I'm wrong becasue for 34 (g o f) I came out with an imaginary number(2)1−1 函數:設A、B為兩個非空集合,f:A→B為一函數,對於任意x1,x2∈A, 若 x 1 ≠ x 2 ⇔ f ( x 1 )≠ f ( x 2 ),則稱函數 f 為1−1 函數。 (3)合成函數:給定兩個函數 f :A→B與 g :B→C,我們定義 f 與 g
Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf
The range of f(x)=(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)+5
The range of f(x)=(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4)+5-Example 2 f(x) = x n where n = 1, 2, 3 d In this example we answer the question "What is x n ?" Once we know the dx answer we can use it to, for example, find the derivative of f(x) = x4 by replacing n by 4 At this point in our studies, we only know one tool for finding derivatives – the difference quotientBeyond simple math and grouping (like "(x2)(x4)"), there are some functions you can use as well Look below to see them all They are mostly standard functions written as you might expect You can also use "pi" and "e" as their respective constants Please




How To Find The Domain Of F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 Quora
Best Answer This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings 100% (1 rating) Transcribed image text Find the inverse function of f f (x) = 7 3x3 f1 (x) = Find the inverse function of f f (x) = x/x 5 f1 (x) = Find the inverse function of f f (x) = 8x 3/ x 5 Find the inverse function of f f (x) = 4 x2, x ge 0 f1 (x) = , xFor example, if f is a function that has the real numbers as domain and codomain, then a function mapping the value x to the value g(x) = 1 / f(x) is a function g from the reals to the reals, whose domain is the set of the reals x, such that f(x) ≠ 0 The range of a function is the set of the images of all elements in the domain Ex13 , 4 If 𝑓(𝑥)=(4𝑥 − 3)6𝑥 − 4, 𝑥 ≠ 23 , show that 𝑓𝑜𝑓(𝑥)=𝑥, for all 𝑥 ≠ 23 What is the inverse of f?
Get an answer for 'Given f(x) and g(x), please find (fog)(X) and (gof)(x) f(x) = 2x g(x) = x3 ' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes∆ la droite d'équation y = 3x et ∆' laThe cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a random variable is another method to describe the distribution of random variables The advantage of the CDF is that it can be defined for any kind of random variable (discrete, continuous, and mixed) Note that the subscript indicates that this is the CDF of the random variable
Weekly Subscription $199 USD per week until cancelled Monthly Subscription $699 USD per month until cancelled Annual Subscription $2999 USD per year until cancelled Thisis 0 when √x2 −1 = √4 − x2 or 2x2 = 5 or x = ± √25 and where f (x) = 2√15 = √6 Hence, range is √3,√6 graph { sqrt (4x^2) sqrt (x^21) 224, 276, 046, 2Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more




F X 3 Find The Numerical Value Of




F X X 3 1 X 3 1 0 X 1 X 2 X 1 0 X 1 Chegg Com
Suppose X has pdf f(x) = 8 < (1 − x2)(3/4) −1 ≤ x ≤ 1 0 else Find the expected value of X Solution Note Similarly to discrete RVs, the expected value is the balancing point of the graph of the pdf, and so if the pdf is symmetric then the expected value is the point of symmetry A sketch of the pdf quickly determines theQuestion This question is from textbook College Algebra I need to find the functions (f o g), (g o f),(f o f), and (g o g) and their domains for 34 f(x) = x^2, g(x) = sqrt(x3) 38 f(x) = 1/sqrt(x), g(x) = x^2 4x Thank you very much!Domain of f(x) = x/(x^21) Natural Language;



Http People Math Harvard Edu Knill Teaching Math1a Handouts Lecture11 Pdf
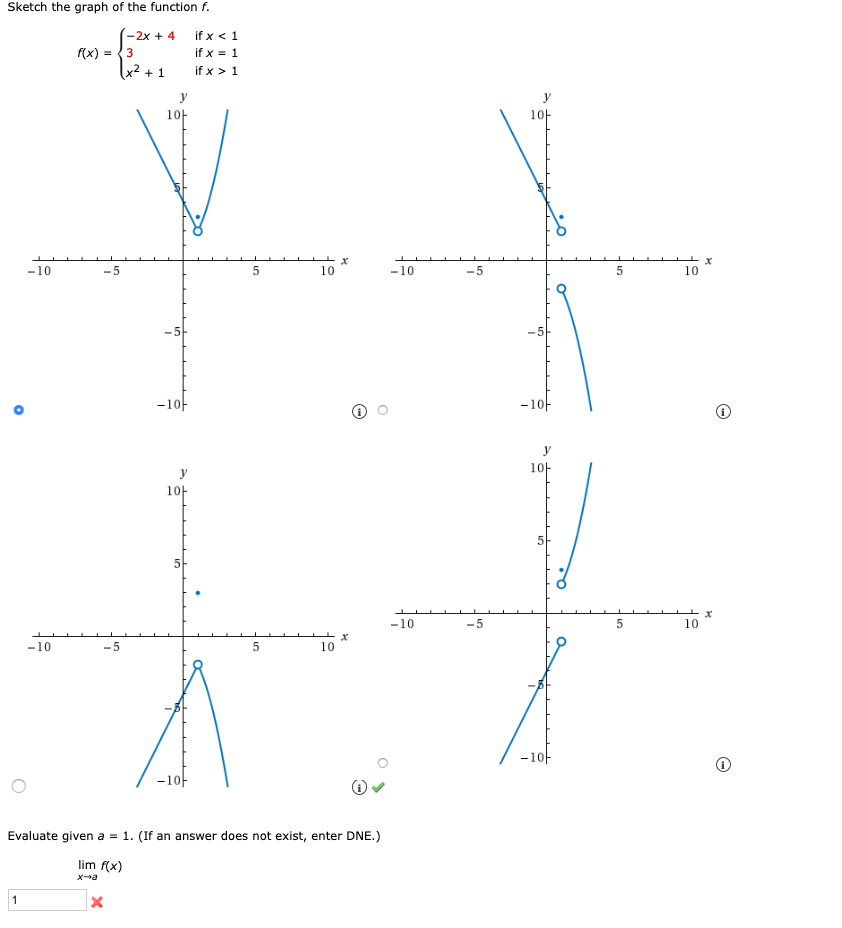



Answered Sketch The Graph Of The Function F Bartleby
Related Queries calculate how drenched I would become if I walked in the rain;آلات حساب للجبر، حساب التفاضل والتكامل، هندسة، إحصاء، وكيمياء مع شرح i made a mistake, i omitted some part while using product rule f(x) = {(3x)/(1x)} 23x taking log on both sides log(fx) = (2 3x) log {(3x)/(1x)}




4 2 Linear Approximations And Differentials Mathematics Libretexts




Consider F R 4 3 R 4 3 Given By F X 4x 3 3x 4 Show That F Is Bijective Find The Inverse Of F And Hence Find F 1 0
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsEg Write input x 2 as x^2 2 Use ^(1/2) for square root ,'*' for multiplication, '/' for division, '' for addition, '' for subtraction Eg1 Write input √x as x^(1/2) 2 Write 5x as 5*x 3 Write x5 as x5 4 Write x 25x as x^25*x 3 Use paranthesis() while performing arithmetic operations Eg1 Write sinxcosxtanx as sin(x)cos(x Ex 12, 10 Let A = R − {3} and B = R − {1} Consider the function f A → B defined by f (x) = ((x − 2)/(x − 3)) Is f oneone and onto?



F X X 2



Http Www Mpsaz Org Rmhs Staff Lxcoleman Trig Test Practice Files Review Chapter 3 Notes Solutions Pdf
Explanation The function is f (x) = 1 √4 − x2 What'under the √ sign must be ≥ 0 and we cannot divide by 0 Therefore, 4 − x2 > 0 ⇒, (2 − x)(2 x) > 0 ⇒, {2 − x > 0 2 x > 0 ⇒, {x < 2 x > − 2𝑓(𝑥)=(4𝑥 − 3)6𝑥 − 4 𝑓(𝑓𝑥) = 4𝑓(𝑥) − 36𝑓(𝑥) − 4 𝑓𝑜𝑓𝑥 = 44𝑥 − 36𝑥 − 4 − 364𝑥 − 36𝑥 − 4Area between y = x^2 and x = 1 and x = 3



How To Solve X 4 2x 3 3x 2 2x 1 0 Manually Quora




How To Find The Domain Of F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 Quora
Chapter 4 Taylor Series 17 same derivative at that point a and also the same second derivative there We do both at once and define the second degree Taylor Polynomial for f (x) near the point x = a f (x) ≈ P 2(x) = f (a) f (a)(x −a) f (a) 2 (x −a)2 Check that P 2(x) has the same first and second derivative that f (x) does at the point x = a 43 Higher Order Taylor Polynomials4 RANDOM VARIABLES AND PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS F(x)= 0 for xF(x) = x2 1 x3 4x is a rational function, it is continuous everywhere in its domain, which is everywhere that the denominator is nonzero The denominator is zero at x= 0 and x= 2 6 If f(x) = (x2 3x)(6x5 2x8), compute f0(1) Solution f0(x) = (2x 3)(6x5 2x8) (x2 3x)(30x4 16x7) f0(1) = 5 4 4 14 = 76 7 For f(x) = 3 p x5 6 p 5 x3




Find The Domain Of The Following Function F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 Log 3 X 1 Sqrt 1 Youtube



Domain Of Definition Of The Function F X 3 4 X 2 Log10 X 3 X Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Solution Steps f ( x ) = x ^ { 4 } ( x 1 ) ^ { 3 } f ( x) = x 4 ( x − 1) 3 Use binomial theorem \left (ab\right)^ {3}=a^ {3}3a^ {2}b3ab^ {2}b^ {3} to expand \left (x1\right)^ {3} Use binomial theorem ( a − b) 3 = a 3 − 3 a 2 b 3 a b 2 − b 3 to expand ( x − 1) 3Here a and x are parameters of my function You need to enter a and x f(2,4) If you want a as a constant parameter eg a=2 f = lambda x 2 * x**2 f(5) if you have a list of input values of x, you can combine map with lambda it is straighforward and easily readable (*map(lambda x 3 * x**2, 1,2,3,4),) or list(map(lambda x 3 * x**2, 1,2(1) lim x!1 x 4 2x3 x2 3 Since this is a polynomial function, we can calculate the limit by direct substitution lim x!1 x4 2x3 x2 3 = 14 2(1)3 12 3 = 7 (2) lim x!2 x2 3x2 (x 2)2 This is a rational function, where both numerator and denominator approach 0 as x approaches 2 We factor the numerator to get lim x!2 x2 3x 2 (x




8 8 Taylor Series Mathematics Libretexts




Find The Values Of K So That The Function F Is Continuous At The Indicated Point F X Kx 1 If X 5 At X 5
2°) Soit g définie sur IR par g(x) = f(x) 3x Déterminer les limites de g en ∞ et en ∞ 3°) Dans un repère orthonormé, soit ( C ) la courbe de la fonction f ;X_0 = 1 y = x 3/2 4x; If f(x) =4x^33x^23x4 then x^3f(1/x) is equal to Maths Relations and Functions NCERT Solutions;




If F X X 2 3 And G X 4x 2 X 4 Find F G X Brainly Com




Misc 13 Find Points F X X 2 4 X 1 3 Has Local Maxima
Given the functions, f(x) = x2 2 and g(x) = 4x 1, perform the indicated operation When applicable, state the domain restriction g(f(x)) 4 x2 1 16 x2 3 4 x2 7 16 x2 8 x 3 Please help I thinks that it is 16 x2 3 calculus for the given functions f and g, find the following and state the domain of each f(x)=square root x;Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Let f = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (0, 1), ( 1, 3)} be a function from Z to Z defined by f(x) = ax b for some(für x = 0 nicht definiert!) f1 x → x1 = 1/x f3 x → x3 = 1/x 3 f5 x → x5 = 1/x 5 f2 x → x2 = 1/x 2 f4 x → x4 = 1/x 4 f6 x → x6 = 1/x 6 Rationale Exponenten (0 n 1) Hier handelt es sich um Wurzelfunktionen Sie sind nur für x ³ 0 definiert Der Graph entsteht, indem man den Graphen der entsprechenden



Riemann Sums And The Definite Integral




Math 432 Hw 2 5 Solutions Pdf Free Download
Let f(x) = {(1 cos 4x)/x2, if x < 0 and a, if x = 0 and √x/(√(16 √x) 4), if x > 0} If f(x) is continuous at x = 0, determine the value of aExamples 2 f(x) = X∞ k=0 (−1)kx2k = 1−x2 x4 −x6 ··= X∞ k=0 (−x2)k = 1 1−(−x2) = 1 1x2, for x < 1 f(x) = X∞ k=0 x2k1 3k = x 1 3 x3 1 9 x5 1 27 x7 ··= x X∞ k=0 x2 3 k = x 1−(x2/3) = 3x 3−x2 for x2/3 < 1 12 Radius of Convergence Radius of Convergence There are exactly three possibilities for a1 Compute the following derivatives (Simplify your answers when possible) x (a) f (x) where f(x) = 1 − x2 1(1 2− x ) 2− (x)(−2x) 1 − x 2x2 1 x2 f (x) = = = (1 2− 2x 2) (1 2− x ) (1 − x )2 1
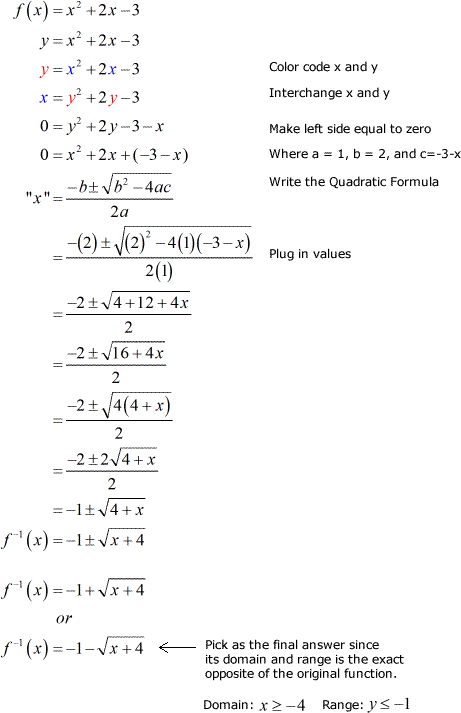



Inverse Of Quadratic Function Chilimath



F X X 2 1 X X 3 X 4 X 1 0 X 2 2 X 3 Askiitians
The function f (x) = 2x^3 – 3x^2 – 12x 4, has A two points of local maximum B two points of local minimum asked in Derivatives by Chandan01 ( 512k points) application of derivativeOsculating circle y = 1/x^2 at x = 2; Find the intervals in which the function f(x) = 3x^4 4x^3 12x^2 5 is (a) strictly increasing (b) strictly decreasing asked in Mathematics by simmi ( 57k points) applications of derivatives




F X X 2 X 2 4 F X X 3 X 2 9 F X Chegg Com




Which Of The Following Functions Best Represents The Graph A F X X 2 X 1 X 2 B F X Brainly Com
Calculadoras gratuitas paso por paso para álgebra, Trigonometría y cálculoX_0 = 1 y = 2x 1/3x 5;Use the distributive property to multiply 3 x 4 − 1 8 x 3 2 4 x 2 by x 1 and combine like terms 3x^{5}15x^{4}6x^{3}24x^{2} 3 x 5 − 1 5 x 4 6 x 3 2 4 x 2
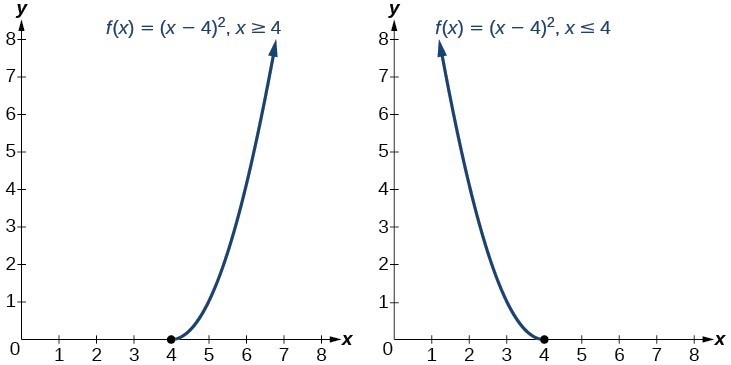



Restrict The Domain To Find The Inverse Of A Polynomial Function College Algebra



Maclaurin S Series
Y = (x^2 2)(x Squareroot x) x_0 = 4 y = (x^2 3)(5 2x^3); f'(x) = (2x3)^3(x^2 x 1)^4(28x^212x7) Looking at the equation, f(x) = (2x3)^4(x^2x1)^5 we first notice a couple patterns 1 The function is a product of two terms 2 Each of the terms is a term with an exponent Since the function is a product of two terms, we know that we have to use the Product Rule to find the first derivative Ex 51, 14 Discuss the continuity of the function f, where f is defined by 𝑓(𝑥)={ (3, 𝑖𝑓 0≤𝑥≤1@4, 𝑖𝑓 1
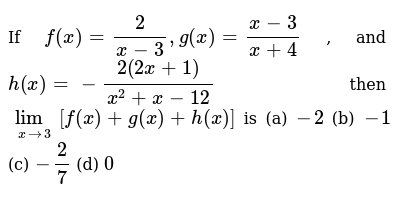



If F X 2 X 3 G X X 3 X 4 And H X 2 2x 1 X 2 X 12 Then Lim X Gt 3 F X G X H X Is A 2 B 1 C 2 7 D 0



Www Shsu Edu Kws006 Precalculus 1 6 Function Inverses Files Ws Soln 1 6a Functioninverses Pdf
X_0 = 0 The normal line to the curve y = f(x) at the with coordinates (x_0, f(x_0)) is the line per the tangent line at P In Exercises 32 through an equation for the normal line to the given the prescribed pointTabelle einfacher Ableitungs und Stammfunktionen (Grundintegrale) Diese Tabelle ist zweispaltig aufgebaut In der linken Spalte steht eine Funktion, in der rechten Spalte eine Stammfunktion dieser Funktion Die Funktion in der linken Spalte ist somit die Ableitung der Funktion in der rechten Spalte Hinweise WennExtended Keyboard Examples Upload Random Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music




Ex 5 5 16 Find Derivative Of F X 1 X 1 X2 1 X4 1 X8




How Do You Find F X Using The Limit Definition Given F X X 2 1 2x 3 Socratic




Rd Sharma Class 9 Solutions Maths Updated For 21 22 Chapter 6 Factorization Of Polynomials
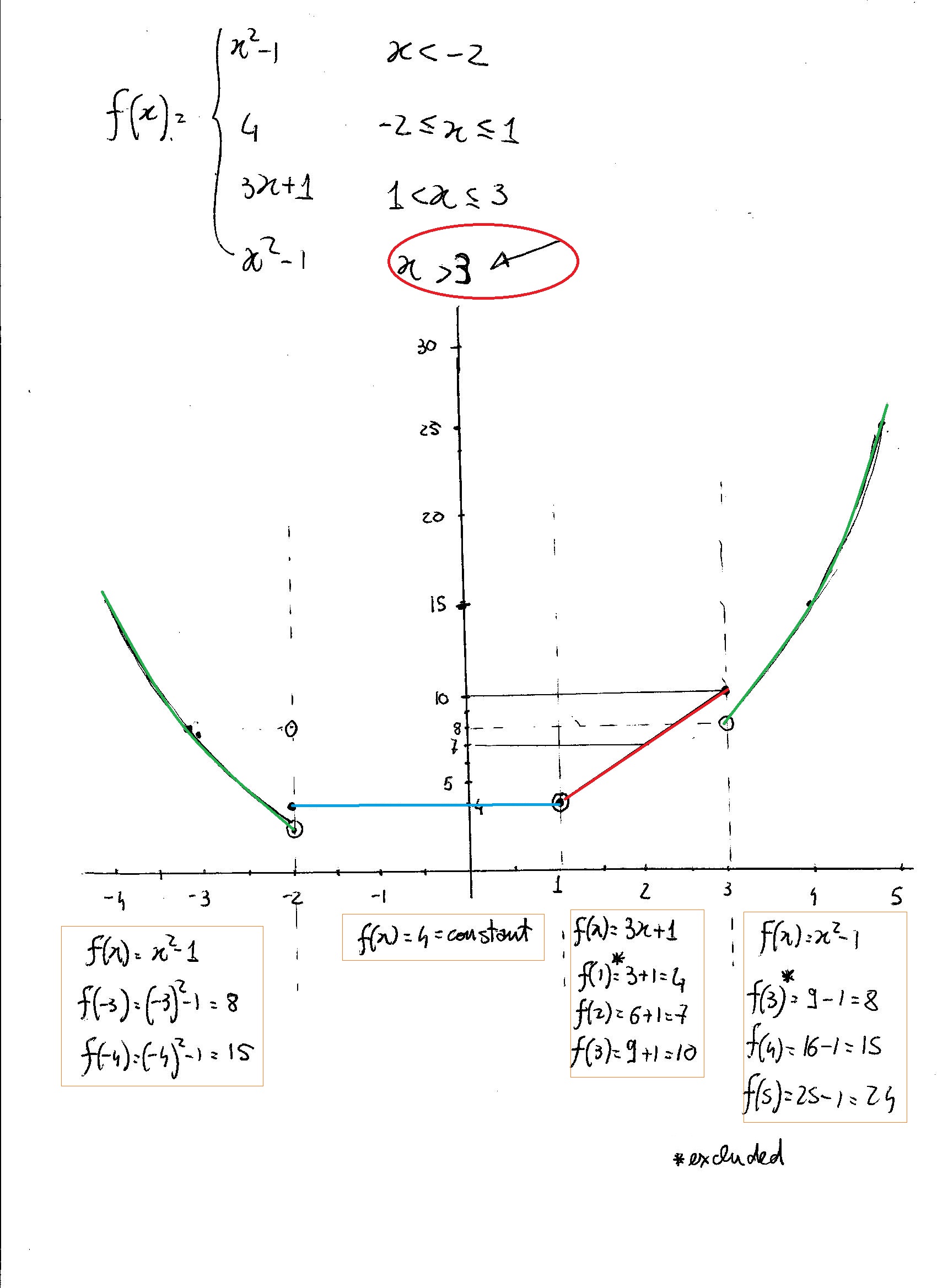



How Would You Graph F X If F X X 2 1 X 2 4 2 X 1 3x 1 1 X 3 X 2 1 X 1 How Would You Evaluate The Function At The Indicated Points F 3 F 2 F 5 F 3 Socratic
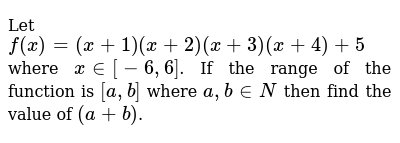



Let F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 5 Where X In 6 6 If The Range Of The Function Is A B Where A B In N Then Find The Value Of A B



Pmt Physicsandmathstutor Com Download Model Answers June 14 Maths June 14 ma c3 edexcel Pdf



Warm Up Find The X And Y Intercepts 1 F X X 4 Ppt Download




Polynomial Functions



What Is The Minimum Value Of Math X 1 2x 1 3x 1 100x 1 Math When Math X Math Is A Real Number Quora




1 2 Solving Equations By The Quadrus Method Levels 1 2 3 G Day Math



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf




Graphs Of Polynomial Functions Algebra And Trigonometry



Sites Levittownschools Com Cbergersen Documents Unit 2 hw answers Pdf



8 5 Approximations Of Roots Of Functions Newton S Method



The Value Of F 0 So That F X 4 X 1 3 Sin X 4 Log 1 X 2 3 Is Continuous Everywhere Is Equal To Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Ex 7 5 4 Integrate X X 1 X 2 X 3 Partial Fractions



Http Www Eastauroraschools Org Cms Lib Ny Centricity Domain 323 Ch 8 review sheet answers Pdf




Answered 5x2 3 24 Y Ur 4 Gre 6 25 Y 7x2 R Io Bartleby



1




Maximum Value Of Function F X Frac X 4 X 2 X 6 2x 3 1 When X 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange




View Question Please Help




Solving Polynomial Equations Answers




Warm Up Exercises 1 What Is The Degree Of F X 8x 6 4x 5 3x 2 Solve X 2 2x 3 0 Answer 6 1 I 2 Ppt Download




F X X 4 X 2 2 F X 2x X 2 1 F X X 2 X Chegg Com




Content Polynomial Function Gallery




Finding Inverse Functions Quadratic Example 2 Video Khan Academy



Modulus Function
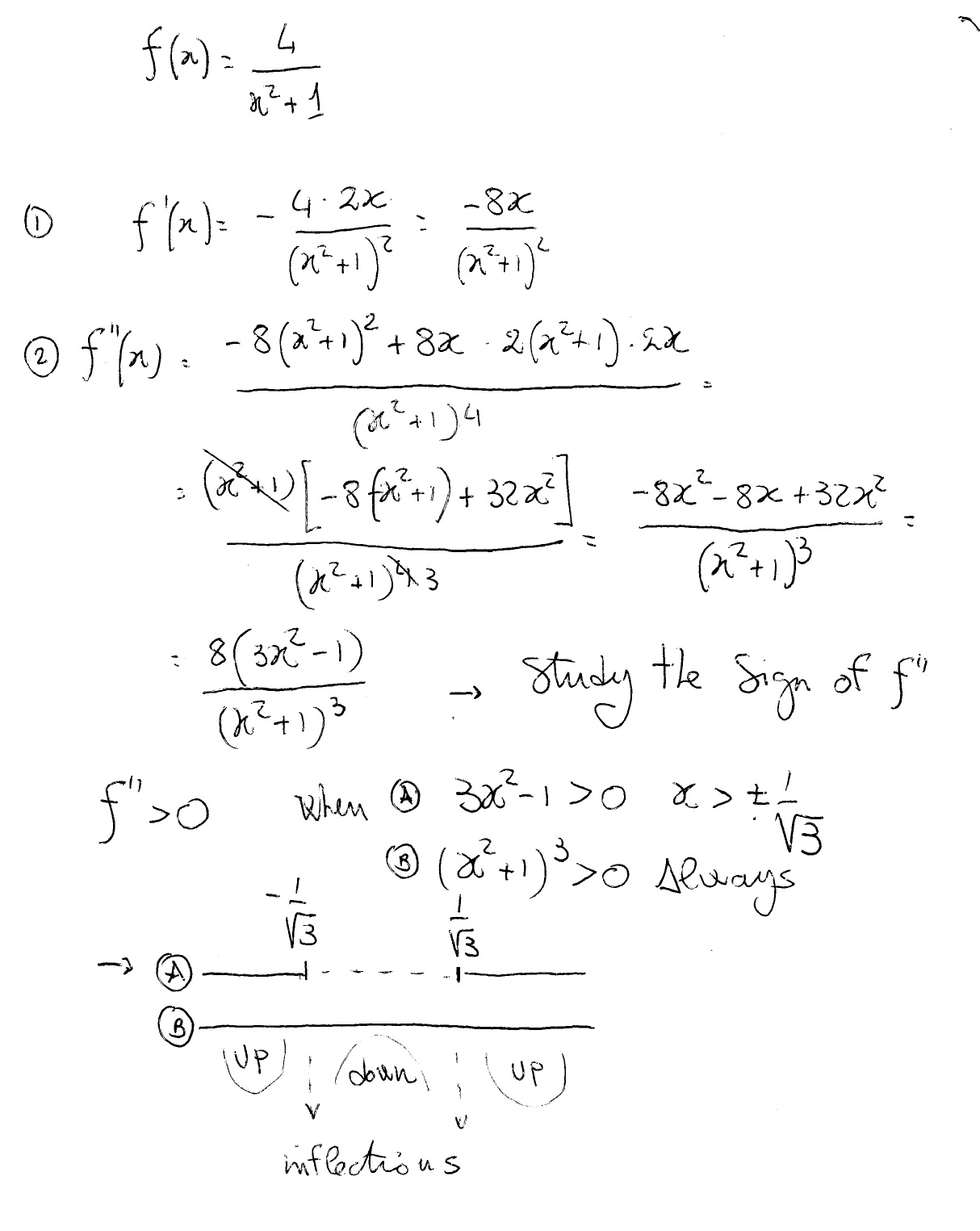



How To Find If A Function F X 4 X 2 1 Is Concave Up Or Concave Down Socratic



8 5 Approximations Of Roots Of Functions Newton S Method
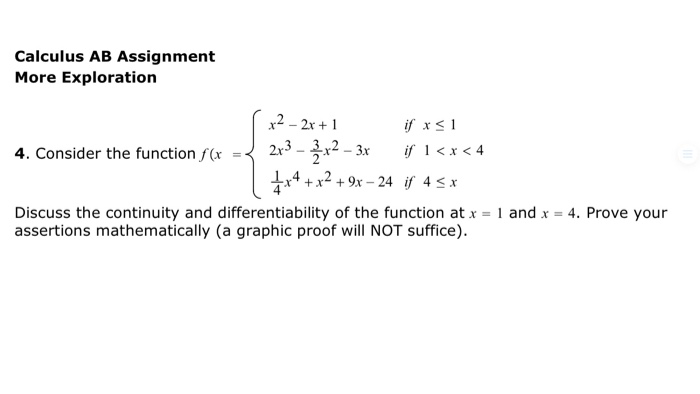



Consider The Function F X X 2 2x 1 If X Chegg Com



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf




اسئلة محلولة عن الدوال والنهايات




If F Mathbb R Setminus 0 1 To Mathbb R Satisfies F X 2f Left Frac 1 X Right 3f Left Frac X X 1 Right X Then 8f 4 Mathematics Stack Exchange



2



Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Standard Topics Various Function Exam Questions Pdf
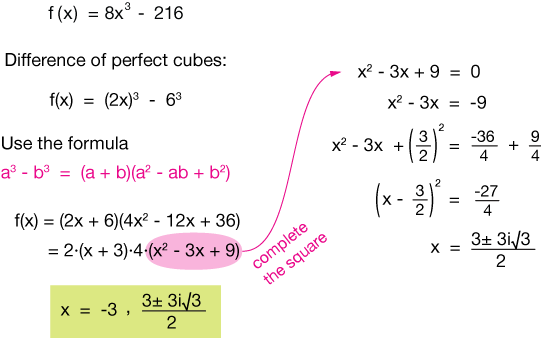



Polynomial Functions
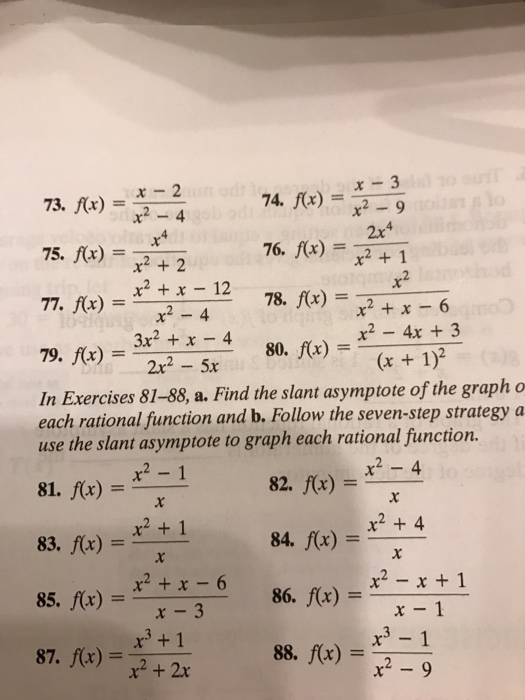



F X X 2 X 2 4 F X X 3 X 2 9 F X Chegg Com




Exercise 1 3 Functions Problem Questions With Answer Solution




Calculus Practicals Maxima And Minima Derivative
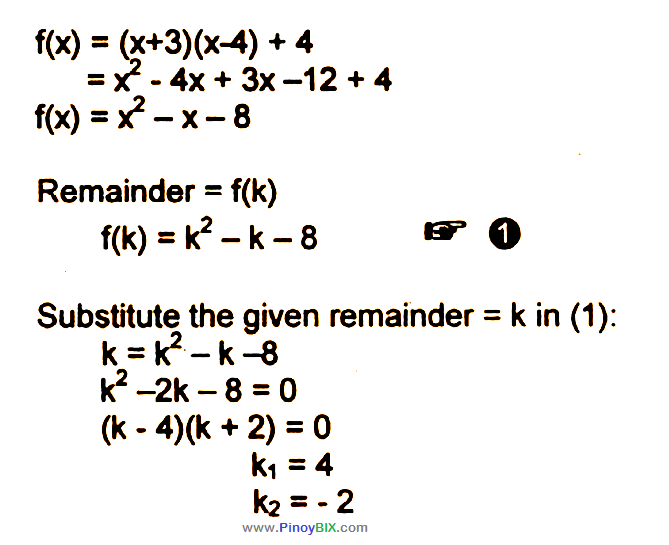



Solution Given F X X 3 X 4 4 When F X Is



Efisd Net Common Pages Displayfile Aspx Itemid




2 Let F X 2x 3 And G X X 4 X In R Find The Following 1 Fof 1 Ii Fog 1 Iii Youtube



Solution Solve The Equation X 3 2x 2 5x 6 0 Given That 2 Is A Zero Of F X X 3 2x 2 5x 6 The Solution Set Is
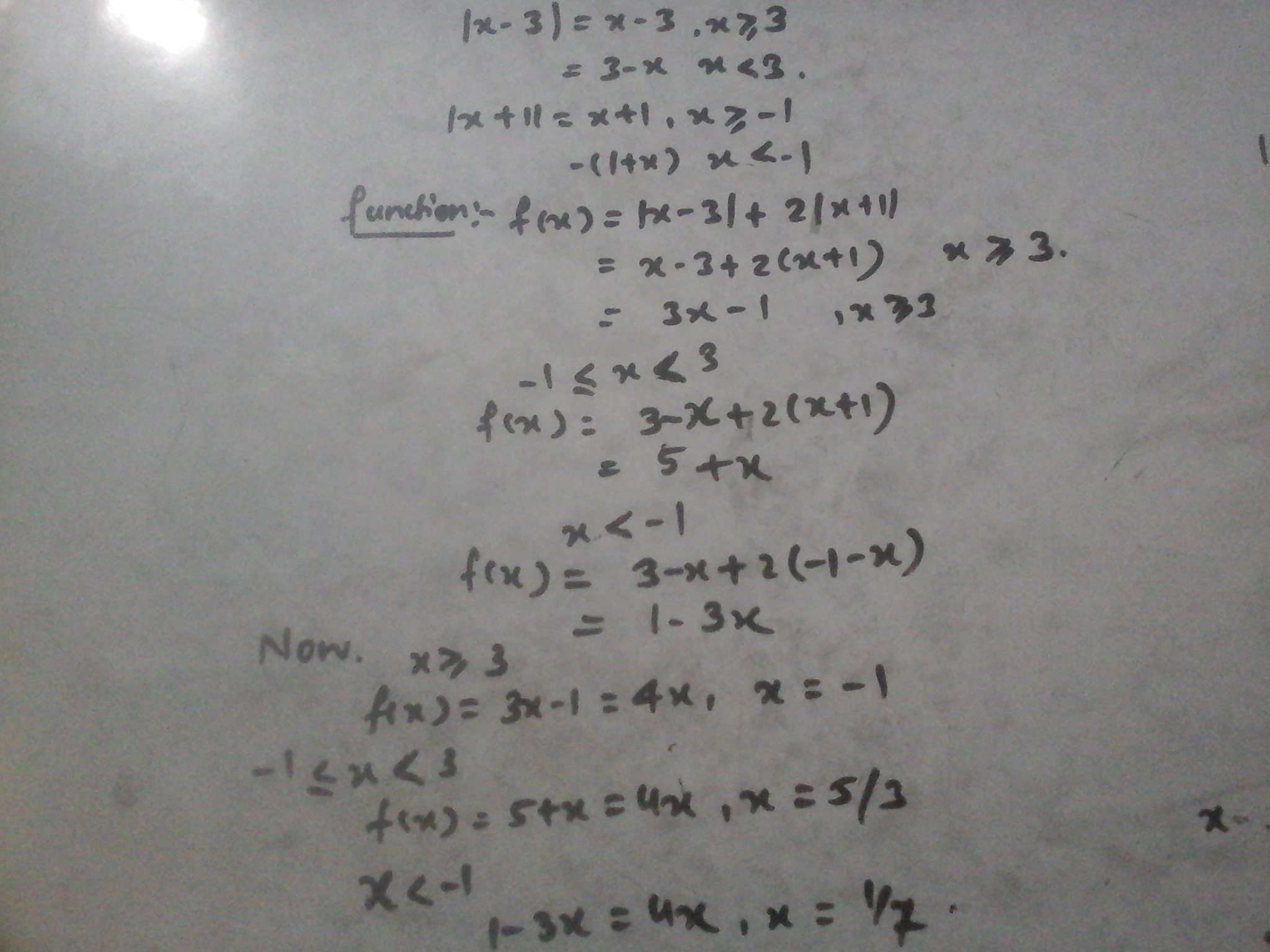



X 3 2 X 1 4 X Askiitians



Solving Polynomial Inequalities Analytically



Redefine The Function F X X 2 2 X 3 X 3 Studyrankersonline




If F X 1 X And G X X 4 Which Of The Following Is The Graph Brainly Com



Q Tbn And9gcqb4oadhn3pwmda4j6x5bcidfo8tdkalmcxgfri4zt13h2b2qzt Usqp Cau




Answered Exercises Find Equations For The Bartleby



Math Scene Equations Iii Lesson 3 Quadratic Equations




Quadratic Function Wikipedia



Www Utdallas Edu Efrom Solhw Pdf




Let F X X 1 X 2 X 3 X 4 5 Where X In 6 6 If The Range Of The Function Is A B Where A B In N Then Find The Value Of A B



2
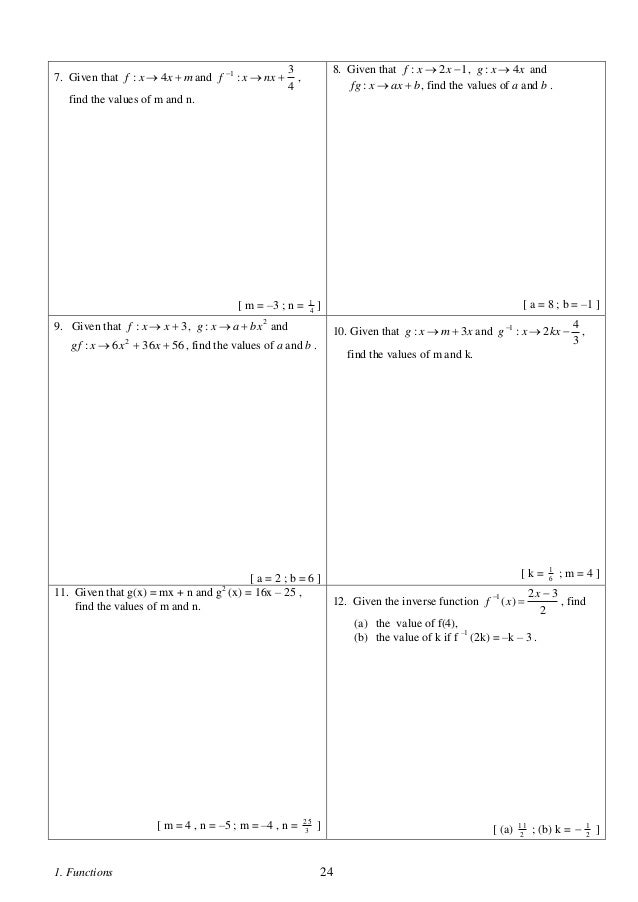



1 Functions



1




Solve This Q Find The Intervals In Which The Function F X 3 Log 1 X Maths Application Of Derivatives Meritnation Com
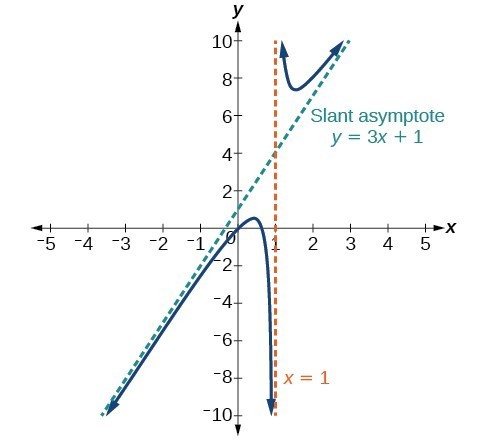



Identify Vertical And Horizontal Asymptotes Math 1314 College Algebra
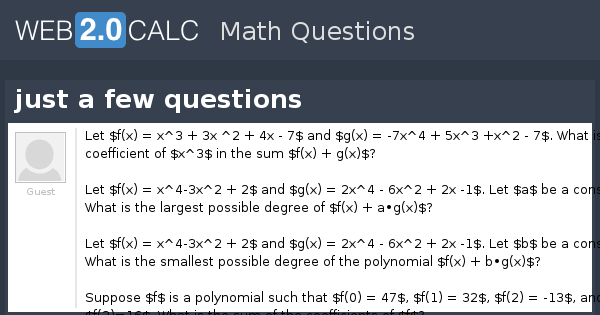



View Question Just A Few Questions
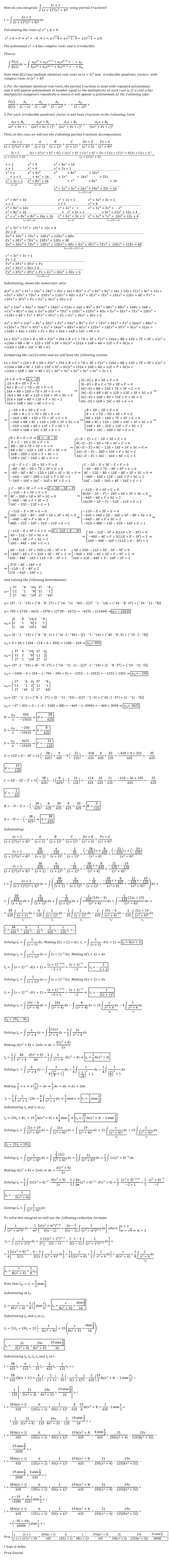



How Do You Integrate Int 2x 1 X 1 3 X 2 4 2 Using Partial Fractions Socratic




Solutions To Graphing Using The First And Second Derivatives




Warm Up Exercises 1 What Is The Degree Of F X 8x 6 4x 5 3x 2 Solve X 2 2x 3 0 Answer 6 1 I 2 Ppt Download




The Islamic University Of Gaza Faculty Of Engineering



Http Www Princeton Edu Mwatson Misc Switz W1 Ex Pdf




Transformations Of The 1 X Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Www Sd308 Org Cms Lib8 Il Centricity Domain 3273 Section 6 1 practice answers Pdf




Binomial Approximation Wikipedia
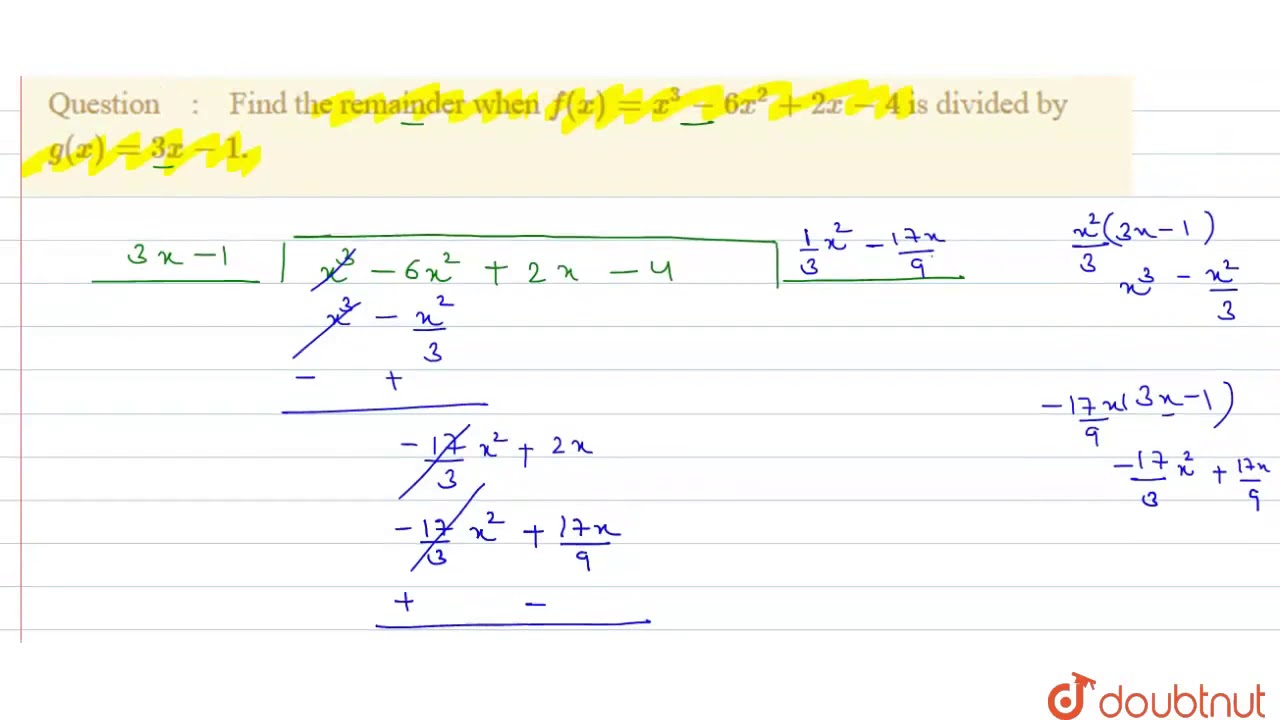



Find The Remainder When F X X 3 6x 2 2x 4 Is Divided By G X 3x 1 Youtube



Graphing Square Root Functions



Sites Levittownschools Com Cbergersen Documents Unit 2 hw answers Pdf




Let F 1 2 Infinity 3 4 Infinity Where F X X 2 X 1 Find The Inverse Of F X Hence Or Otherwise Solve The Equation X 2 X 1 Maths Relations And Functions Meritnation Com




If F X 1 X X 1 2x X X 1 X 1 X 3x X 1 X X 1 X 2 X X 1 X 1 Then F 50 F 51 Youtube




If The Function F R R Defined By F X 4 X4 X 2 Then Show That F 1 X 1 F X And Hence Deduce The Value Of F 14 2f 12 F 34
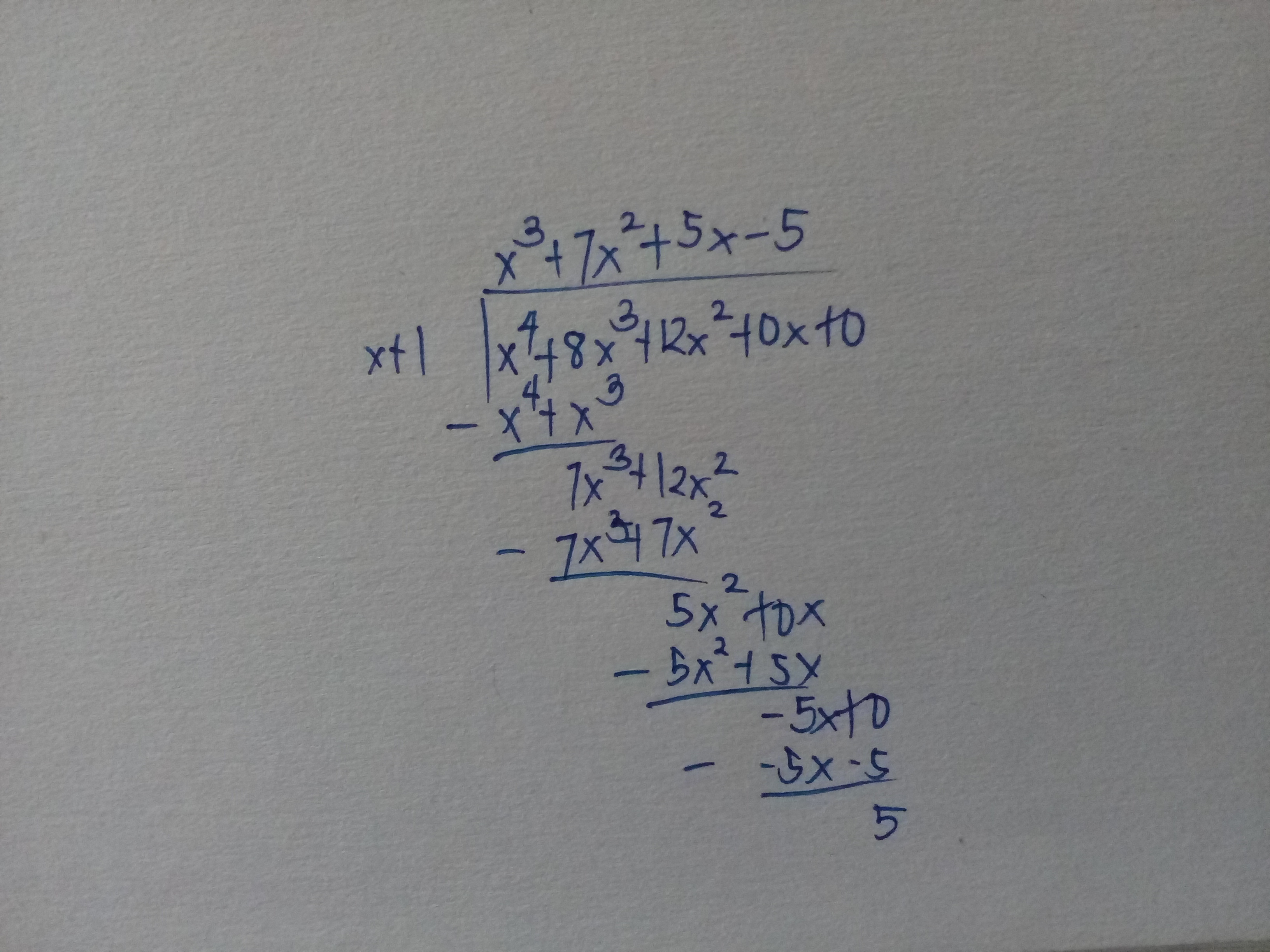



How Do You Find The Remainder When F X X 4 8x 3 12x 2 X 1 Socratic




Multiplying And Dividing Functions Article Khan Academy



How To Find F 2 If F X 2 5x 4 X 3 Quora




1 Functions




14 If F X 1 X X 3 1 X 3 4 X 2 1 X 2 13 The



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿